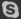In the current UPS system, the valve-controlled sealing lead-acid-free maintenance battery is characterized by a large amount of energy than the conventional lead-acid battery, which has a large energy volume ratio, good discharge performance, and small maintenance work. However, in the actual operation, due to many reasons, the battery will have a malfunction, a housing deformation, and a reduction in capacity, which will not only reduce the service life, but also seriously affect the reliability of the power system. According to statistics, 40% -50% of the fault in the UPS power system is caused by the reasons for the battery.
In the current UPS system, the valve-controlled sealing lead-acid-free maintenance battery is characterized by a large amount of energy than the conventional lead-acid battery, which has a large energy volume ratio, good discharge performance, and small maintenance work. However, in the actual operation, due to many reasons, the battery will have a malfunction, a housing deformation, and a reduction in capacity, which will not only reduce the service life, but also seriously affect the reliability of the power system. According to statistics, 40% -50% of the fault in the UPS power system is caused by the reasons for the battery.1 Valve-controlled sealed acid accumulates the structure and working principle of lead batteries
The above is the structure of the battery:
1) Anode (positive electrode): The contained in the form of an anode active substance (PBO2).
2) Cathode (negative electrode): The filling of the cathode active material (PB) is filled.
3) Substrate: The electrolyte inside is dilute sulfuric acid (H2SO4).
4) Safety Valve:
1 Keep the battery to increase the ingestion efficiency.
2 In the case where the internal pressure is normal, the outside air is prevented from entering the battery.
3 When an excessive gas is generated, the valve is automatically opened to prevent explosion.
4 Prevent electrolyte evaporation, avoid drying of the battery.
5) Chemical equations:
PBO2 + PB + H2SO4 = 2PBSO4 + 2H2O
6) Working principle: The charging and discharge process of the battery is the process of electrical energy and chemical energy in the battery. At the time of charging, the positive and negative electrode is converted from the lead of the lead, and the sponge lead will be stored in the positive electrode, and when the discharge is discharged; the positive and negative electrodes are converted from the lead, the sponge-shaped lead is converted into sulfuric acid. Lead is converted to electrically converted into electrical energy to the load, and the chemical reaction process is represented by the formula.
2 troubleshooting
Although it is called the maintenance battery, it means that there is no need to add the acid, add water, measurement, etc. during use, and the maintenance is not equal to the maintenance, and the maintenance is directly determined by the battery life, the following may Fault analysis:
1) Vulneak: There is an obvious electrolyte out of the electrolyte outflow or overflow in the initial use of use (within 2 years). There are mainly housing drain and safety valve leakage.
Cause: It is possible that the outer casing of the battery is leaked (there is a sand or crack) or a safe valve leak (in the battery, generating a gas inside during charging, so that the electrolyte floats, resulting in acid from the safety valve). This situation is generally related to the process design and quality of the battery manufacturer.
Hazard: This will not only affect the capacity of the battery, but also flow out or overflow caused corrosion to the battery and battery cabinet, but also causes pollution to the surrounding environment.
2) Cladder: Generally occurring in the medium, late. The electrolyte slowly seeps from the pole column at the end of the battery.
Cause: This is likely to be poorly resistant to corrosion resistance, producing PBSO4 in the reaction of sulfuric acid, resulting in expansion of its volume, resulting in a structure loose, resulting in diffusion of sulfuric acid.
Hazard: This will not only make the pole column slowly thinner, and its internal resistance will gradually increase, not able to withstand the discharge of the large current when discharge.
3) Leakage: Also internal and external gas exchange.
Cause: This may be that the safety valve is damaged or not in place. This situation is generally related to the process design and quality of the battery manufacturer.
Hazard: Due to the air leak, the internal gas amount cannot achieve the design value, resulting in hydrogen from precise, which causes the moisture in the electrolyte, gradually dry, the internal resistance of the battery increases, and finally the battery is scrapped.
4) Dry: Mainly in use, in the later, expressed as the end voltage of the battery, and the capacity is insufficient.
Reason: The battery is not good, the floating charge voltage is too high; on the other hand, it may be related to the production manufacturer to prevent the battery from using the initial extraction of acid from using the initial drain acid.
Hazard: The battery internal resistance increases to scrap the battery.
5) Heat out of control: When the battery reaches the end of the life, the electrolyte is gradually exhausted in the battery. At this time, the positive electrode plate grid gradually corroded, the battery capacity may fall quickly, and it is possible to have a thermal out of control. The phenomenon of leakage.
Reason: Mainly in the case of high temperature ambient temperature, due to the battery is a sealed entity, the process of charging is heat dissipation, the internal temperature is increased due to endurance, resulting in an increase in charging current, and the internal resistance is lowered. , Vicious circulation until the housing of the battery is severely deformed, expanded, and cracking. Finally, the battery will be scrapped. Although the thermal out of control does not occur frequently, it should be paid attention to the phenomenon of battery heating. It is a fire. The occurrence of a fire. The occurrence of fire is mainly caused by two reasons: one is because the positive electrode plate corrosion is exposed to the negative plate, causing internal short circuits, and the battery is fired; The other is because the positive electrode plate corrosion elongation or thermal out of control causes the internal electric tank to expand, causing damage to the electric trough, and the battery is leakage.
6) Over (under) charging: Excessive charging voltage will result in hydrogen in electrolyte, and generate "electrolysis water", the electrolysis reaction causes temperature rise, limited by heat dissipation conditions, and most of the heat Increasing the reaction speed, it can destroy the entire battery in a short period of time; on the other hand, when the number of gas generated by the electrolytic reaction exceeds the critical value, the battery will be rolled out through the safety valve, resulting in "water loss", if more than 10%, extreme The board is cracking, eventually leading to the raised, scrapped. If it is charged, then the internal active substance is not effective, which causes electrode plate sulfate, causing the resistance to increase.
7) Excessive discharge: This can result in a large amount of sulfate in the battery to be adsorbed to the surface of the cathode, forming sulfate of the battery anode plate, due to the lead of sulfate is an insulator, causing a bad impact on charge and discharge. The more sulfate of the plate, the larger the internal resistance of the battery, the worse the chargeable dischargeability of the battery. Every time the battery is over, it will lead to a decline in the actual battery capacity. As the number of times is increasing, the actual capacity of the battery pack has continuously declined. Once the city is interrupted, the actual reserve schedule of the battery is far less than the original design value.
3 maintenance of battery
Through the above analysis, the cause of the failure may be the battery's own design problem, or it may be caused by the necessary maintenance, but in any case, it is the primary problem with the normal operation of the equipment, so there is the following maintenance of the battery:
1) Avoid overcharge: UPS can be regulated.
2) Prevent excessive discharge: UPS can be regulated.
3) Appropriate discharge of the battery properly.
4) Pay attention to the temperature and humidity of the machine room: 22 ¡ã C; 40%.
5) Regular examination.
4 Conclusion
The above is to analyze the possible failures of the valve-controlled sealing lead-acid-free maintenance battery, although the UPS battery used in our central power station did not have the above failure, but for the duty personnel, only the possible failure, and Quickly exclude it to ensure the normal and safety of power.
Article from: http://www.brcpower.com Recommend: LiFePO4 Battery Manufacturer Energy storage battery Manufacturer Integrated machine energy storage battery series Manufacturer Lead lithium battery Manufacturer Outdoor Backup Battery Manufacturer Portable outdoor power supply Manufacturer Power battery Manufacturer Powerwall LiFePO4 Battery Manufacturer Battery rack Manufacturers Telecom LiFePO4 Battery Manufacturer Wall mounted battery storage Manufacturer China Lifepo4 Battery